

AIM 1: Define and compute the yield-based DV01.
1、The magnitude of the percentage price change on a bond for a given change in interest rates depends on all of the following EXCEPT the:
A) volatility of interest rates.
B) coupon rate.
C) term to maturity.
D) initial yield.
The correct answer is A
The volatility of interest rates will affect the frequency with which price changes are observed, but not the magnitude. All else equal, bond price sensitivity is higher for (a) lower coupon bonds; (b) longer term maturity bonds; and (c) lower the initial yield.
AIM 2: Discuss the differences in applying and interpreting the effective duration, modified duration and Macaulay duration.
1、A five-year bond selling at par and yielding 6 percent has a duration of 3.2 years. If interest rates rise one percent, what will be the market price of the bond?
A) 96.8.
B) 97.0.
C) 103.0.
D) 103.2.
The correct answer is A
Percent change in price = -(3.2) (0.01) = -3.2%. We are told the bond is currently selling at par, or 100. The new price will be 96.8.
2、One of the features of using only modified duration for estimating change in price is that the size of the estimated price change is:
A) the same for up or down movements in interest rates.
B) higher for an up move in interest rates as compared to a down move in interest rates.
C) lower for an up move in interest rates as compared to a down move in interest rates.
D) higher for a callable bond as compared to an option-free bond.
The correct answer is A
Estimated price changes using only duration are symmetric for a change in interest rates. How the modified duration for a callable bond would compare with an otherwise identical option-free bond will depend upon the relevant range over which the measure would be calculated. If the relevant range includes a range in which the callable bond will experience price compression, the effective duration measure for the callable bond will be lower than for the option-free bond.
3、A 6-year, 5 percent annual coupon bond with $100 par value currently trades at par and has an effective duration of 4.25 years. What is the price change if the yield falls by 50 basis points?
A) 2.13%.
B) 4.25%.
C) -4.25%.
D) 6.38%.
The correct answer is A
Percentage price change = (-) (effective duration)( Δy)
= (-)(4.25)(-0.005) = 2.125%
4、Community Bank has a $5 million par value position in a bond with the following characteristics:
The bond is a 5-year, zero-coupon bond.
The bond is priced to yield 5%.
The historical mean change in daily yields is 0.0%.
The standard deviation in yield is 36 basis points.
The modified duration of the bond is closest to:
A) 4.395.
B) 2.524.
C) 5.000.
D) 4.878.
The correct answer is D
The modified duration is:
Remember that while the Macaulay duration for a zero-coupon bond is the same as its maturity, an adjustment needs to be made for modified duration.
5、Consider a semiannual pay bond with two years to maturity, a 6 percent coupon, and a yield to maturity of 8 percent.
The Macaulay and modified duration of this bond are closest to:
A) 1.91 and 1.84.
B) 1.94 and 1.86.
C) 1.96 and 1.84.
D) 1.86 and 1.74.
The correct answer is A
|
Term |
Cash Flow |
PV of Cash Flow |
Time-Weighted PV |
|
0.5 |
3 |
2.8846 |
1.4423 |
|
1.0 |
3 |
2.7737 |
2.7737 |
|
1.5 |
3 |
2.6670 |
4.0005 |
|
2.0 |
103 |
88.0448 |
176.0896 |
|
|
|
$96.3701 |
$184.3061 |
DMAC = $184.3061 / $96.3701 = 1.91; DMOD = 1.91/ 1.04 = 1.84
The convexity of this bond, based on a change in the yield to maturity of 50 basis points (i.e., Dy = 0.5%), is closest to:
A) 4.15.
B) 4.75.
C) 4.94.
D) 2.08.
The correct answer is A
Based on bond values at yields to maturity of 7.5% and 8.5%,
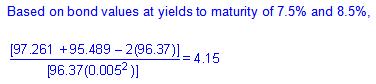
6、Of the following, the bond with the lowest Macaulay duration is the:
A) 10%, 10-year Treasury.
B) 8.5%, 10-year Treasury.
C) 10-year, zero-coupon corporate.
D) 10%, perpetual pay (consol) bond.
The correct answer is A
Both the consol and the corporate have a 10-year duration. The 10% coupon Treasury has a shorter duration than the 8.5% Treasury because coupon and duration are inversely related, all else equal.
7、Estimate the Macaulay and modified durations of a 2-year, annual-pay bond paying a 6 percent coupon and priced to yield 5 percent.
A) 2.00; 1.90.
B) 1.94; 1.85.
C) 6.00; 5.00.
D) 1.05; 1.06.
The correct answer is B
|
Macaulay Duration | ||||
|
N |
CF |
PV of CFw |
% of total |
N ′ % of total |
|
1 |
$6 |
$5.7143 |
0.0561 |
0.0561 |
|
2 |
$106 |
$96.1451 |
0.9439 |
1.8878 |
|
|
$101.8594 |
1.0000 |
1.9439 | |
modified duration = (1.9439 / 1.05) = 1.8513
8、The Macaulay and modified duration of a 2-year annual pay bond paying an 8 percent coupon and priced to yield 10 percent are closest to:
A) 1.75; 1.92.
B) 8.00; 10.00.
C) 1.92; 1.75.
D) 1.08; 1.10.
The correct answer is C
|
N |
CF |
PV of CF |
% of total PV |
N x % of total PV |
|
1 |
$8 |
$7.2727 |
0.0753 |
0.0753 |
|
2 |
$108 |
$89.2562 |
0.9247 |
1.89494 |
|
Sum |
|
$96.528 |
1.000 |
1.9247≈1.92 |
AIM 6: Create a barbell and a bullet portfolio.
1、Immunization is the process of offsetting the effects of interest-rate changes on the value of assets and liabilities. Coverage of liabilities with significant convexity may be more effectively matched with a:
A) mortgage portfolio, especially in a highly volatile rate environment.
B) barbell portfolio with positive convexity.
C) bullet portfolio with little convexity.
D) callable bond portfolio, especially in a declining-rate environment.
The correct answer is B
Barbell portfolios usually contain substantial convexity, which can be used to offset changes in liabilities not met with duration matches.
AIM 7: Analyze the impact convexity may have on a barbell and bullet portfolio.
1、Evaluated at the same yield, the investment that is expected to have the greatest convexity is a:
A) portfolio with a duration of 10 that contains a 5-year zero-coupon bond and a 15-year zero-coupon bond.
B) callable 6% coupon bond of 10-year duration.
C) 6% coupon bond of 10-year duration.
D) 10-year zero-coupon bond.
The correct answer is A
A barbell portfolio will have greater convexity than a bullet portfolio, so convexity of the barbell portfolio is greater than the convexity of the 10-year zero-coupon bond. In general, the higher the coupon, the lower the convexity, so convexity of the 10-year zero-coupon bond is greater than the convexity of the 6% coupon bond of 10-year duration and the callable 6% coupon bond of 10-year duration.

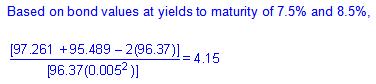
| 欢迎光临 CFA论坛 (http://forum.theanalystspace.com/) | Powered by Discuz! 7.2 |